Breast Cancer and Breast Repair (Breast Reconstruction)

You may have had or are about to have a mastectomy because you’ve been diagnosed with breast cancer or some sort of breast tumor (even benign but cause a breast distortion). Or you are at very high risk of developing it in the future. If this is the case, you need to learn about options to rebuild your breast or breasts — a surgery called breast reconstruction.
In fact, you are not the only person who is experiencing this condition. Many women underwent these circumstances and they are also ready to transfer their experience to tell you ‘this is not the end of the road but a new beginning’. It’s normal to feel anxious, uncertain, sad, and mournful about giving up a part of your body that was one of the hallmarks of becoming a woman. But again, this is not the end of the road.

Typically, breast reconstruction takes place during or sometimes after mastectomy. Breast reconstruction also can be done many months or even years after mastectomy (or lumpectomy). During reconstruction, we create a breast shape using an artificial implant (implant reconstruction), a part of tissue from another place on your body (autologous reconstruction), or both.
I want to talk you through each of the reconstruction options, what’s involved, and any risks, as well as alternatives to reconstruction.
Beast reconstruction is an operation to try to get back the shape of the breast. Reconstruction of a breast that has been removed due to cancer or other disease is one of the most rewarding surgical procedures available today.
Breast reconstruction can be done:
1/ after breast cancer surgery i.e. mastectomy (removal of a breast), lumpectomy (removal of part of the breast), or
2/ after any type of trauma, burn deformity or injury that resulted in a deformity of the breasts.
The aim of breast reconstruction is to match the remaining natural breast as closely as possible. This can either be done by creating a breast ‘form’ with an implant, which is put underneath the skin and muscle that covers your chest, or by using skin, fat (and sometimes muscle) from another part of your body. A combination of these techniques is used for some women.
Doctors differ in their views about the best timing for breast reconstruction. Most prefer to do it at the same time as the initial breast cancer surgery. Other doctors believe it is important to wait for a while, possibly a year or more after having a breast removed, if radiotherapy is being considered after mastectomy. Waiting before the reconstruction may also give a woman time to come to terms with the emotional effects of the cancer.
Some women find that reconstruction carried out at the same time as their initial surgery, helps them to cope with the emotions that are normally associated with the loss of a breast, and to get back to a normal life again. Reconstruction has no known effect on the recurrence of disease in the breast, nor does it generally interfere with chemotherapy or radiation treatment, should cancer recur. Your surgeon may recommend continuation of periodic mammograms on both the reconstructed and the remaining normal breast. If your reconstruction involves an implant, be sure to go to a radiology center where technicians are experienced in the special techniques required to get a reliable x-ray of a breast reconstructed with an implant. Scans and x-rays of the breast area are still possible and if the cancer comes back in the breast area, this can still be detected.
It is possible to create a new nipple and this is usually done as a separate operation once the reconstructed breast has settled into its final shape. However, this does not have to be done unless you wish.
There are four main types of breast reconstruction:
- Reconstruction using an implant
- Skin expansion. The most common technique combines skin expansion and subsequent insertion of an permanent implant.
- Tissue flap reconstruction, in which skin, muscle and fat from your back or abdomen (tummy) is transferred to the chest to create a new breast.
- Free flap reconstruction, in which skin and fat from your lower abdomen, or occasionally buttock, is grafted to the breast area. The skin and fat is completely removed from the original area and a new blood supply is created for the new breast tissue, using microsurgery.
- 1. Reconstruction using an implant:
One of the ways that a breast can be reconstructed is with an implant. A breast implant is a round or tear drop shaped, flexible silicone shell filled with either salt water or silicone gel. Breast implants can either be placed over the chest muscle or under the chest muscle. We prefer to place the implant under the muscle to give a more natural result and prevent any complication i.e. capsule formation ( at least to reduce the possibility of)

Implant reconstruction may be a good option for you if:
- you have enough healthy skin and tissue to cover and support a breast implant
- you’d like to avoid extra scars on the other parts of your body that happen with flap reconstruction
- you prefer shorter surgery and recovery time than the time needed for flap reconstruction
- you do not need radiation therapy (there is a high chance of developing problems like seroma or similar problems with implant reconstruction after radiation)
2. Reconstruction using your own Tissue: The other main type of breast reconstruction uses tissue transplanted from your body, such as your belly, bacak, thighs, or buttocks, to form a breast shape. More plastic surgeons have experience with breast implant surgery than with flap reconstruction
Breast reconstruction can give you a good cosmetic result, but reconstructed breasts may not have the same look or feel as your original breasts. It’s also important to know that most women lose sensation in their breast area after mastectomy.
a. Breast Reconstruction with LD (Latissimus dorsi ) Muscle Flap
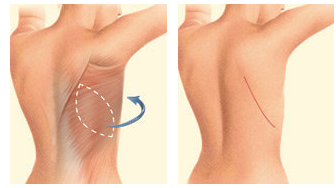
This muscle is located in your back. It’s the muscle that helps you do twisting movements, such as swinging a racquet or golf club. In this surgery, an oval flap of skin, the fat underneath it and the muscle is used to reconstruct the breast. This flap is moved under your skin around to your chest.
Because the origin of transfer is closer to the chest, the latissimus dorsi flap may be a good reconstruction choice for women who are not good candidates for TRAM, DIEP, or SIEA flaps.
The latissimus dorsi flap may be a good option for women with small- to medium/small-sized breasts. This surgery leaves a scar on your back, but most surgeons try to place the incision so the scar is covered by your bra strap.
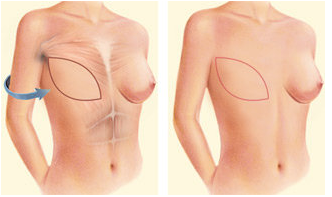
b. Breast Resonstruction with TRAM flap:
TRAM stands for transverse rectus abdominis, a muscle in your lower abdome. A flap of this skin, fat, and “6-pack” muscle are used to reconstruct the breast in a TRAM flap procedure.
Overall, TRAM flaps are the most commonly performed type of flap reconstruction, partly because TRAM flap tissue is very similar to breast tissue and makes a good substitute.
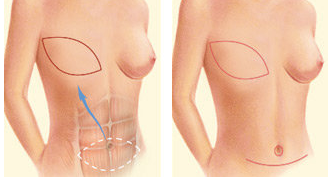
There are two main types of TRAM flaps:
- Free TRAM flap: In a free TRAM flap, fat, skin, blood vessels, and muscle are cut from the wall of the lower belly and moved up to your chest to rebuild your breast.
- Pedicled (or attached) TRAM flap: In a pedicled TRAM flap, fat, skin, blood vessels, and muscle from your lower belly wall are moved under your skin up to your chest to rebuild your breast.
Because skin, fat, muscle, and blood vessels are moved from the belly to the chest, having a TRAM flap means your belly will be flatter and tighter — as if you had a tummy tuck. In most cases, the scar is below your bikini line.
ANCILLARY SURGERIES : If you’re having a mastectomy and consecutive reconstruction on only one breast, your breasts may not be symmetrical after surgery. If you’d like, you can choose to surgically alter your healthy breast so it will better match the reconstructed breast in size and shape. But even after that they will not be fully symmetrical as this is the nature of normal breast.
